Do you feel a sharp, burning pain in the ball of your foot when you walk? Does it often feel like you’re standing on a small pebble or a fold in your sock, but when you check, there’s nothing there? This classic, frustrating sensation is a hallmark symptom of a common condition called Morton’s Neuroma.
This nerve-related issue can make walking, running, or even standing painful, but it is highly treatable. Understanding the cause of the pain is the first step toward finding the right solution. This guide will cover the causes, symptoms, and treatments to help you get back on your feet comfortably.
Table of Contents
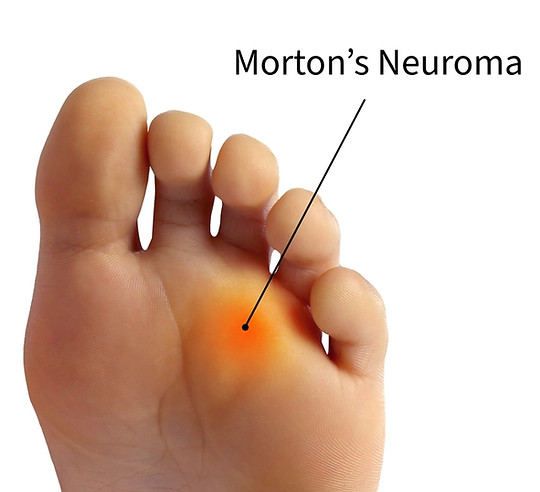
What Is Morton’s Neuroma?
Despite its name, Morton’s Neuroma is not a true neuroma or tumor. It is a benign (non-cancerous) condition where the tissue surrounding a nerve in your foot thickens and becomes inflamed. This thickened, irritated nerve is the source of the pain.
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), this condition, also known as an interdigital neuroma, most commonly occurs on the nerve between the third and fourth toes. The compression and irritation of this nerve lead to the distinct symptoms of pain and discomfort.
Common Causes of Morton’s Neuroma
At its core, Morton’s Neuroma is caused by anything that leads to chronic compression, irritation, or injury to the nerve between your toes. The thickening is the body’s response to this repeated stress.
Common causes and contributing factors include:
- Poor Footwear: This is a primary culprit. Wearing high-heeled shoes, or shoes that are tight, narrow, or pointed in the toe box, squeezes the toe bones together and compresses the nerve.
- Foot Structure: Certain foot types are more prone to developing a neuroma. These include flat feet (pes planus), high arches (pes cavus), bunions, and hammertoes, all of which can cause instability and pressure.
- High-Impact Activities: Repetitive stress from activities like running or sports that involve a lot of time on the balls of the feet can irritate the nerve.
- Foot Injury: A previous trauma or injury to the foot can contribute to the development of a neuroma.
Key Symptoms of Morton’s Neuroma
Symptoms usually start gradually and may come and go, often aggravated by wearing certain shoes or engaging in specific activities. There is typically no visible or outward sign, like a lump.
The key symptoms include:
- The “Pebble in the Shoe” Sensation: The most classic symptom is the feeling like walking on a marble or a fold in your sock, right in the ball of your foot.
- Pain in Ball of Foot: A sharp, burning, or shooting pain that is centered in the ball of the foot and may radiate out to the neighboring toes (usually the 3rd and 4th).
- Numbness or Tingling: You may feel numbness, “pins and needles,” or tingling in the affected toes.
- Aggravation and Relief: The pain is often worse when walking or wearing tight shoes and is typically relieved by taking off the shoes, stopping the activity, and rubbing the foot.
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase your likelihood of developing this condition:
- High-Heeled or Tight Shoes: This is the strongest risk factor, which is why the condition is far more common in women.
- High-Impact Sports: Runners, dancers, and court-sport athletes are at higher risk.
- Foot Deformities: People with existing bunions, hammertoes, or flat feet.
Diagnosis: How It’s Found
A diagnosis is often made based on your unique description of the symptoms and a physical exam.
- Patient History: Explaining the “pebble” sensation and how your pain is linked to footwear is a key part of the diagnosis.
- Physical Exam: A doctor will press on the ball of your foot and squeeze the area to check for a tender spot or a “click” (known as a Mulder’s sign), which can reproduce the pain.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: These are often ordered first to rule out other problems, such as a stress fracture or arthritis.
- Ultrasound or MRI: As the Mayo Clinic notes, these imaging tests are very effective at visualizing the soft tissue and can definitively show the thickened nerve (neuroma).
Treatment Options for Morton’s Neuroma
Treatment for Morton’s Neuroma almost always begins with conservative, non-surgical methods aimed at relieving pressure on the nerve.
Conservative (Non-Surgical) Treatment
- Footwear Change: This is the most important first step. Stop wearing tight, narrow, or high-heeled shoes. Switch to shoes with a wide toe box, low heels, and good cushioning.
- Orthotics and Padding: Your doctor may recommend over-the-counter or custom-molded shoe inserts (orthotics). A simple “metatarsal pad” placed under the ball of the foot can be very effective at spreading the metatarsal bones and reducing pressure on the nerve.
- Rest and Activity Modification: Take a break from high-impact activities (like running) that aggravate the pain.
- Ice: Applying an ice pack to the bottom of your foot for 15-20 minutes can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Medication: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) can help manage pain and inflammation.
Medical and Surgical Treatment
If conservative measures don’t provide enough relief, your doctor may suggest:
- Injections: A corticosteroid injection directly into the area of the neuroma can provide powerful, fast-acting relief from inflammation. In some cases, this may be all that is needed.
- Decompression Surgery: A surgeon makes an incision to relieve the pressure on the nerve by cutting a nearby ligament.
- Neurectomy (Nerve Removal): This is a last resort if all other treatments fail. The surgeon removes the inflamed, thickened portion of the nerve. This permanently relieves the pain but will also result in permanent numbness in the affected toes.
Prevention Tips
You can reduce your risk of developing Morton’s Neuroma by being kind to your feet:
- Choose Shoes Wisely: Wear shoes that have a wide toe box and a low heel.
- Limit High Heels: If you wear high heels, try to limit the time you spend in them and choose styles with a wider toe.
- Use Proper Athletic Shoes: Ensure your running or sports shoes are a good fit and replace them when they become worn out.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: This reduces the overall stress and pressure on your feet.
When to See a Doctor
You should make an appointment with your healthcare provider or a podiatrist (foot specialist) if:
- You have persistent pain in the ball of your foot that lasts for more than a few days and doesn’t improve with rest or a change in shoes.
- The pain is severe, getting worse, or interfering with your ability to walk.
- You experience ongoing numbness or tingling in your toes.
Don’t ignore the “pebble in your shoe.” Getting a proper diagnosis and starting simple treatments early can prevent the condition from worsening and get you back to walking pain-free.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Published on August 3, 2023 and Last Updated on October 30, 2025 by: Priyank Pandey
Get real time update about this post category directly on your device, subscribe now.