Graves disease is an autoimmune disorder that results in the overproduction of thyroid hormones. The most common symptom of Graves disease is hyperthyroidism, which can cause a number of symptoms including weight loss, anxiety, and insomnia. Graves’ disease can be treated with medication or surgery, but it is important to see a doctor if you think you may have the condition.
While there is no cure for Graves’ disease, it can be treated with medication and lifestyle changes. With treatment, most people with Graves’ disease are able to live normal, healthy lives.
Causes
There is no one definitive answer to what causes Graves’ disease, as there is a variety of contributing factors. However, it is generally agreed that the root cause is an overactive immune system. This can be due to a viral infection, or it may be an inherited trait. Additionally, women are more likely than men to develop Graves’ disease, and it is most commonly diagnosed in people between the ages of 20 and 40.
There are several possible triggers for an overactive immune system in people who are predisposed to Graves’ disease. These triggers may include stress, pregnancy, puberty, menopause or taking certain medications (such as beta-blockers or lithium). Once the immune system is activated, it begins producing antibodies that attack the thyroid gland.
Symptoms
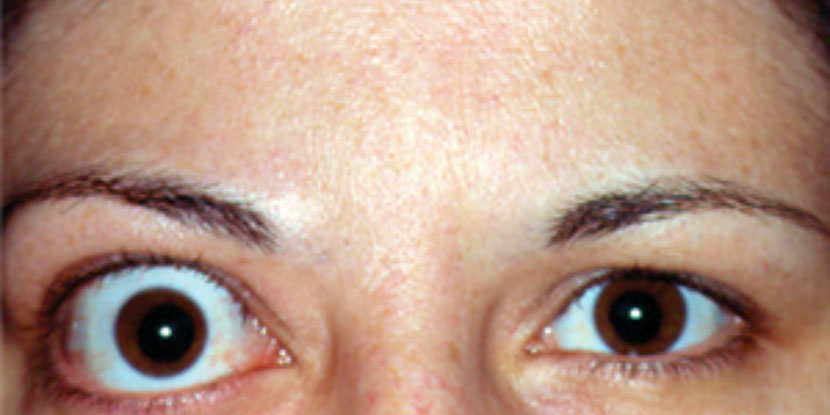
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that results in the overproduction of thyroid hormones. The most common symptom of Graves’ disease is hyperthyroidism, which can cause a number of symptoms including weight loss, anxiety, irritability, and difficulty sleeping. Graves’ disease can also cause goiters, or an enlargement of the thyroid gland. In severe cases, Graves’ disease can lead to graves orbitopathy, which is a condition that causes inflammation and pressure on the eyes.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of Graves’ disease is typically made based on symptoms and a physical examination. Blood tests can also be helpful in diagnosing the condition by measuring levels of thyroid hormones and antibodies. An imaging test called a radioactive iodine uptake scan may also be used to help diagnose Graves’ disease.
Treatment
Although there is no cure for Graves’ disease, treatment options are available to manage the condition. Radioactive iodine is often used to destroy the overactive thyroid cells and shrink the gland. Antithyroid medications can also be used to help control hormone levels. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the thyroid gland entirely.
With proper treatment, most people with Graves’ disease are able to live normal, healthy lives. It is important to work with a doctor or endocrinologist to develop a treatment plan that works for you.
Published on August 12, 2022 and Last Updated on August 12, 2022 by: Priyank Pandey