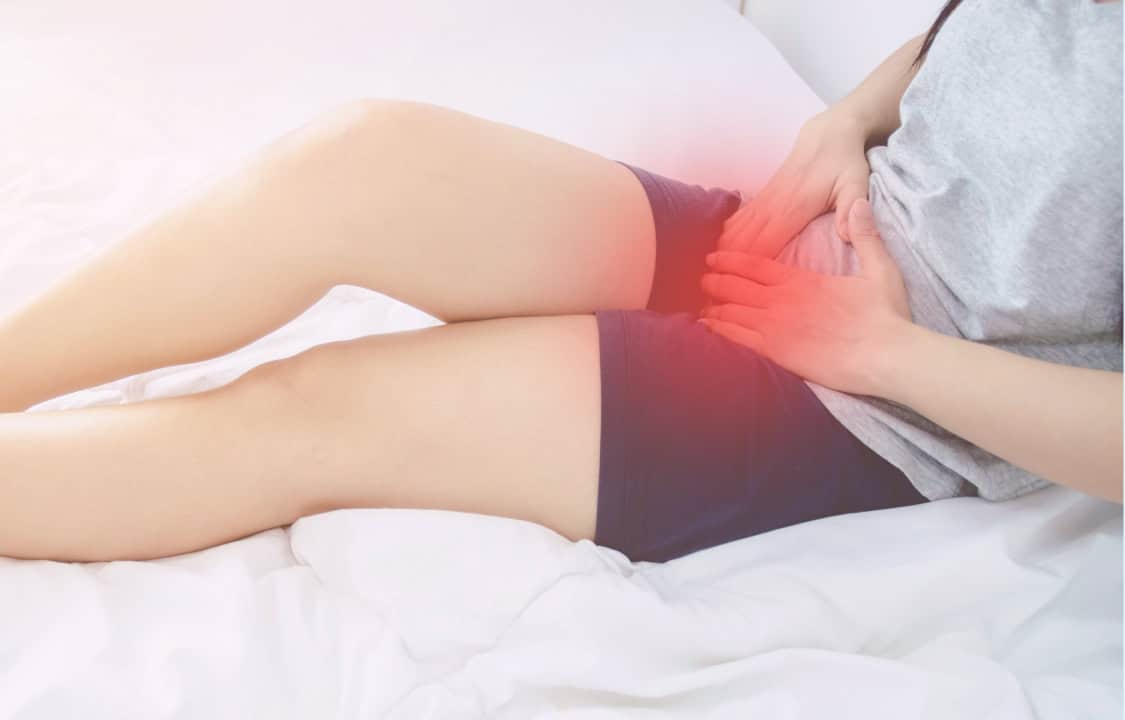
Experiencing a burning sensation after sex can be painful, confusing, and deeply concerning. Instead of feeling close to your partner, you’re left with discomfort that can range from mild irritation to severe pain. This symptom, known as burning after sex or postcoital dysuria/pain, is a clear sign that something is irritating or inflaming your body.
The good news is that you are not alone, and this is a common issue with many treatable causes. The causes of burning after intercourse can be different for men and women, but they often point to infection, irritation, or friction.
This guide will walk you through the most common reasons for this symptom, other signs to watch for, and what you can do to find relief.
Table of Contents
What Is Burning After Sex?
Burning after sex refers to any pain, stinging, or burning sensation felt in the genital area (vagina, vulva, or penis) or urinary tract (urethra) either during or immediately following sexual intercourse.
This discomfort can be:
- External: Felt on the skin of the vulva (the outer female genitals) or the shaft/head of the penis. This is often due to friction or an allergic reaction.
- Internal: Felt deep inside the vagina or as painful urination after sex. This often points toward an infection or internal inflammation.
Understanding the type and location of the burning can provide important clues about its underlying cause.
Common Causes of Burning After Sex
The reasons for this painful symptom are different for men and women.
Common Causes in Women
- Vaginal Dryness / Friction: This is one of the most common causes. When the vagina is not sufficiently lubricated, the friction from intercourse can cause microscopic tears in the vaginal and vulvar tissue, leading to a raw, burning feeling. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), causes of dryness include hormonal changes (menopause, breastfeeding), certain medications, and insufficient arousal.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Sexual activity is a primary risk factor for UTIs. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) explains that intercourse can push bacteria from the genital area into the urethra, leading to an infection of the bladder (cystitis). The main symptom is often painful urination after sex.
- Vaginal Infections (Vaginitis): Inflammation of the vagina is a major culprit.
- Yeast Infections: An overgrowth of Candida fungus causes intense itching, burning, and a thick, white discharge.
- Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): An imbalance of vaginal bacteria, leading to a thin, grayish discharge, a “fishy” odor, and burning.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Many STIs can cause inflammation that leads to burning. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), infections like chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, and genital herpes can all present with symptoms of painful urination or genital burning.
- Allergic Reactions or Sensitivity: The delicate skin of the genitals can react to various products. Common irritants include:
- Latex in condoms
- Ingredients in lubricants or spermicides
- Harsh soaps, detergents, or douching products
Common Causes in Men
- Urethritis: This is an inflammation of the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body). The CDC notes that the most common cause of urethritis in men is an STI, particularly gonorrhea or chlamydia. This leads to penile burning after sex, especially during urination.
- Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate gland can cause pain in the pelvis and genitals, which can be worsened by ejaculation, leading to a burning sensation.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): While less common in men than in women, men can still get UTIs that cause burning and a frequent urge to urinate, especially after sex.
- Friction or Allergic Reaction: Just like in women, insufficient lubrication can cause friction burn. Men can also have allergic reactions to condoms, lubricants, or a partner’s vaginal products.
- Balanitis: This is inflammation of the head of the penis, often caused by poor hygiene or an infection (fungal or bacterial), which can be severely irritated by sexual activity.
Key Symptoms Associated with Post-Intercourse Burning
Burning after sex is often just one piece of the puzzle. Look for these other related symptoms:
- Pain or stinging when you urinate
- A frequent or urgent need to urinate, even if little comes out
- Cloudy, dark, or foul-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Itching, redness, or swelling of the vulva, vagina, or penis
- Abnormal discharge (e.g., thick and white like cottage cheese, or thin and gray/green)
- The appearance of new sores, blisters, or bumps
- Pain during intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Fever, chills, or lower back pain (This could signal a kidney infection, which is a medical emergency).
Diagnosis: Finding the Cause
To get the right treatment, you must have the right diagnosis. A doctor will likely:
- Discuss Your Medical History: They will ask about your symptoms, sexual partners, and the products you use (soaps, lubes, condoms).
- Perform a Physical Exam: A doctor will examine the genital area for signs of redness, swelling, discharge, or sores. For women, this often includes a pelvic exam.
- Order Tests:
- Urine Test (Urinalysis): This is the primary test to check for a UTI by looking for white blood cells and bacteria.
- Vaginal Swab: A sample of vaginal discharge can be examined under a microscope to diagnose a yeast infection, BV, or trichomoniasis.
- STI Screening: Urine tests or swabs can accurately test for STIs like chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Treatment Options for Burning After Sex
Treatment is targeted directly at the diagnosed cause.
- For UTIs: A course of antibiotics will clear the infection.
- For Yeast Infections: Antifungal medications, available as over-the-counter creams (like miconazole) or a prescription oral pill (like fluconazole).
- For Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): Antibiotics, typically metronidazole or clindamycin, as a gel or pill.
- For STIs: Specific antibiotics or antiviral medications will be prescribed depending on the infection. It is vital that your partner(s) also get tested and treated.
- For Vaginal Dryness:
- Using a high-quality, water-based or silicone-based lubricant during sex.
- For persistent dryness from menopause, a doctor may recommend over-the-counter vaginal moisturizers or prescription vaginal estrogen therapy.
- For Allergic Reactions: The treatment is to identify and avoid the irritant. This may mean switching to latex-free (polyurethane) condoms or using a hypoallergenic, unscented lubricant.
Risk Factors for Developing This Symptom
You may be at a higher risk for experiencing burning after sex if you:
- Are female (due to a shorter urethra, making UTIs more likely)
- Have new or multiple sexual partners
- Are post-menopausal
- Have a history of UTIs, yeast infections, or BV
- Use irritating products like douches or scented soaps
- Do not use adequate lubrication during sex
Prevention Tips: How to Stop Burning After Sex
You can take proactive steps to reduce your risk:
- Urinate Before and After Sex: This is one of the most effective ways to prevent UTIs. The Urology Care Foundation recommends this to help flush bacteria out of the urethra.
- Use Lubricant: If friction is an issue, be generous with a body-safe lubricant.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps dilute your urine and flush bacteria from your urinary tract.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Gently wash the genital area with warm water before and after sex. Avoid harsh soaps and never douche, as douching disrupts the healthy vaginal flora, per the Office on Women’s Health (OWH).
- Choose Products Wisely: Opt for unscented, hypoallergenic soaps, detergents, and menstrual products.
- Get Regular STI Screenings: If you are sexually active, regular testing is a key part of maintaining your health.
When to See a Doctor
While mild irritation from friction may resolve on its own, you should consult a healthcare professional if:
- The burning is severe or lasts more than 24 hours.
- You have symptoms of an infection (fever, abnormal discharge, foul-smelling urine).
- You see blood in your urine.
- You have sores, blisters, or a rash.
- This is a recurring problem every time you have sex.
- You suspect you may have been exposed to an STI.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Published on January 15, 2025 and Last Updated on October 29, 2025 by: Priyank Pandey
Get real time update about this post category directly on your device, subscribe now.