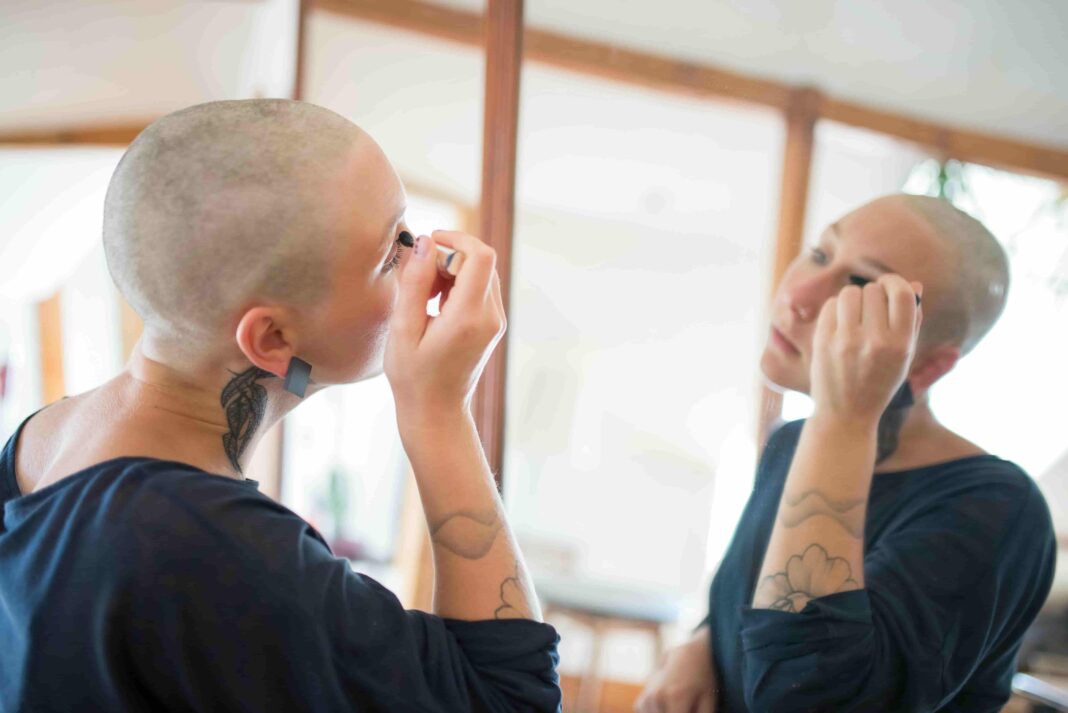
Alopecia, a term that encompasses various forms of hair loss, can have a profound impact on an individual’s physical appearance, self-esteem, and quality of life. While commonly associated with genetic factors, alopecia can arise from a range of underlying causes, including autoimmune disorders, hormonal imbalances, and environmental triggers. Understanding the complexities of alopecia is essential for both those affected by the condition and healthcare professionals seeking to provide effective treatment options. It’s time to delve into the causes, manifestations, and available treatments for alopecia.
Understanding Alopecia: A Complex Condition
Alopecia manifests in different forms, each characterized by its unique pattern and severity of hair loss. Androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness, is the most common type and is primarily attributed to genetic factors and hormonal imbalances. This condition typically results in progressive thinning of hair on the scalp, often leading to a receding hairline or bald patches. Alopecia areata, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to sudden, patchy hair loss on the scalp, face, or other parts of the body. This form of alopecia can vary in severity, with some individuals experiencing small, localized patches of hair loss, while others may lose all of the hair on their scalp (alopecia totalis) or their entire body (alopecia universalis).
Other Manifestations
Less common forms of alopecia include telogen effluvium. This occurs when a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting (telogen) phase of the hair growth cycle simultaneously. It results in the excessive shedding and thinning of hair, eventually causing traction alopecia. This occurs as a result of repeated pulling or tension on the hair follicles. It’s often due to tight hairstyles or hair grooming practices.
Exploring the Causes of Alopecia
The underlying causes of alopecia areata in women are multifaceted and can vary depending on the specific type of hair loss. In cases of androgenetic alopecia, genetic predisposition, and hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a central role in the development of the condition. DHT, a potent form of testosterone, can bind to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually cease producing hair. In autoimmune forms of alopecia, such as alopecia areata, the exact cause remains unclear, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Research suggests that genetic predisposition, along with triggers such as stress, illness, or environmental toxins, may contribute to the onset of autoimmune reactions targeting the hair follicles.
Exploring Treatment Options
Treatment options for alopecia vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, as well as individual factors such as age, gender, and overall health. In cases of androgenetic alopecia, topical medications containing minoxidil, a vasodilator that promotes hair growth, are often prescribed to slow down hair loss and stimulate the regrowth of hair. For more advanced cases of androgenetic alopecia, oral medications such as finasteride, which inhibits the production of DHT, may be recommended to prevent further hair loss and promote thicker, healthier hair growth. Additionally, advanced treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy have shown promising results in stimulating hair regrowth.
A Quest for a Better Life
In cases of alopecia areata, treatment options may include corticosteroid injections. This reduces inflammation and suppresses the immune response. Also, topical immunotherapy using chemicals like diphencyprone or squaric acid dibutyl ester can be employed to trigger an allergic reaction and stimulate hair regrowth. Systemic immunosuppressive medications can be used in the most severe cases. While there is no definitive cure for alopecia, ongoing research into the underlying mechanisms of the condition and the development of innovative treatment modalities offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life..
Conclusion
Alopecia is a complex and multifaceted condition that can have significant physical and emotional impacts on individuals affected by it. Fortunately, there is a lot that patients can do to address the issue now. Ongoing research and advancements in treatment modalities hold promise for the development of more effective therapies and ultimately, a better quality of life for individuals affected by alopecia.
Published on April 5, 2024 and Last Updated on April 5, 2024 by: Priyank Pandey